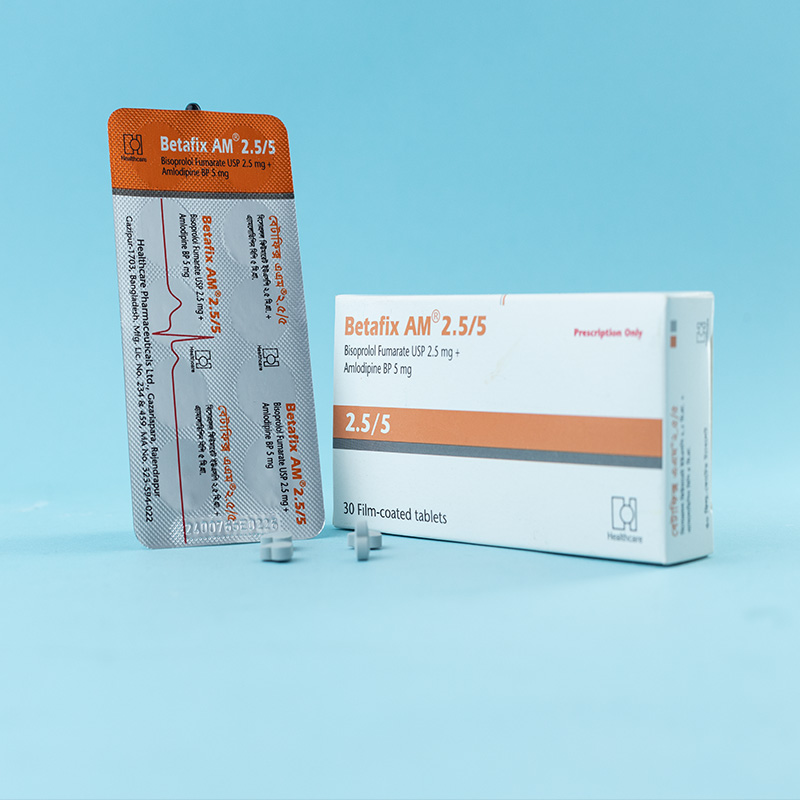
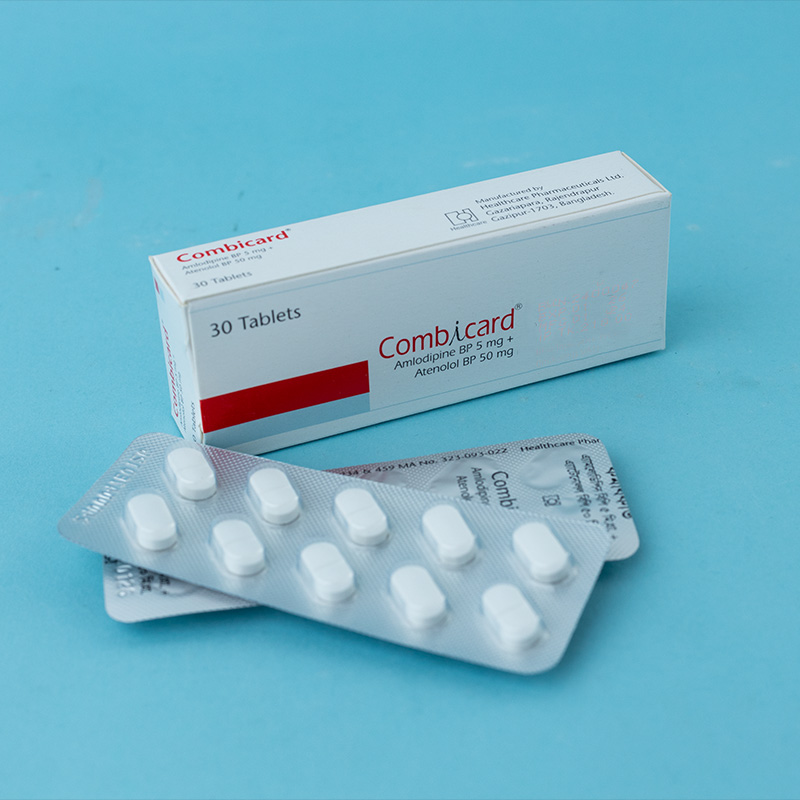
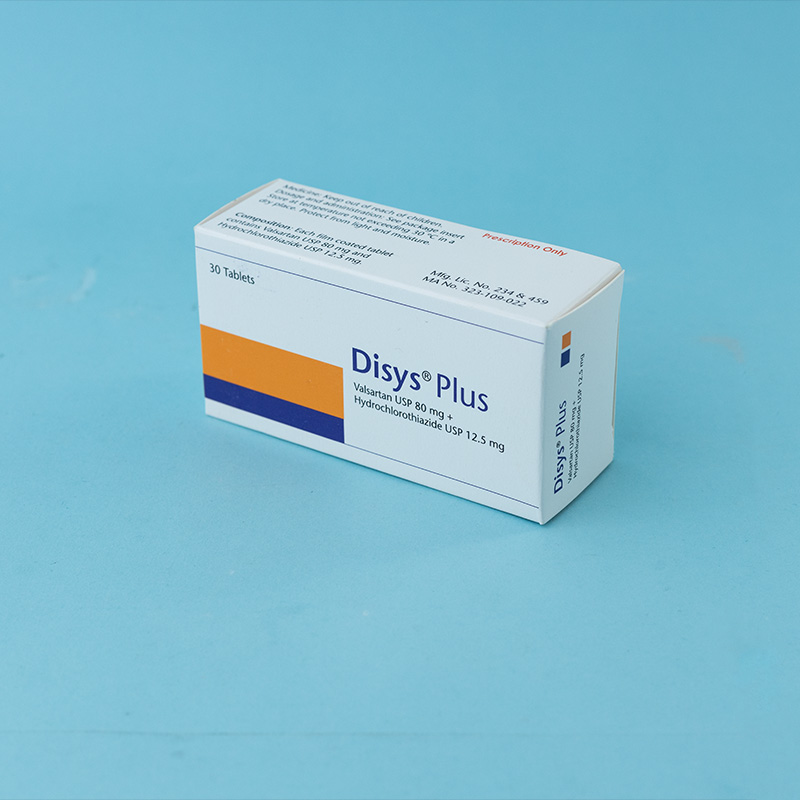
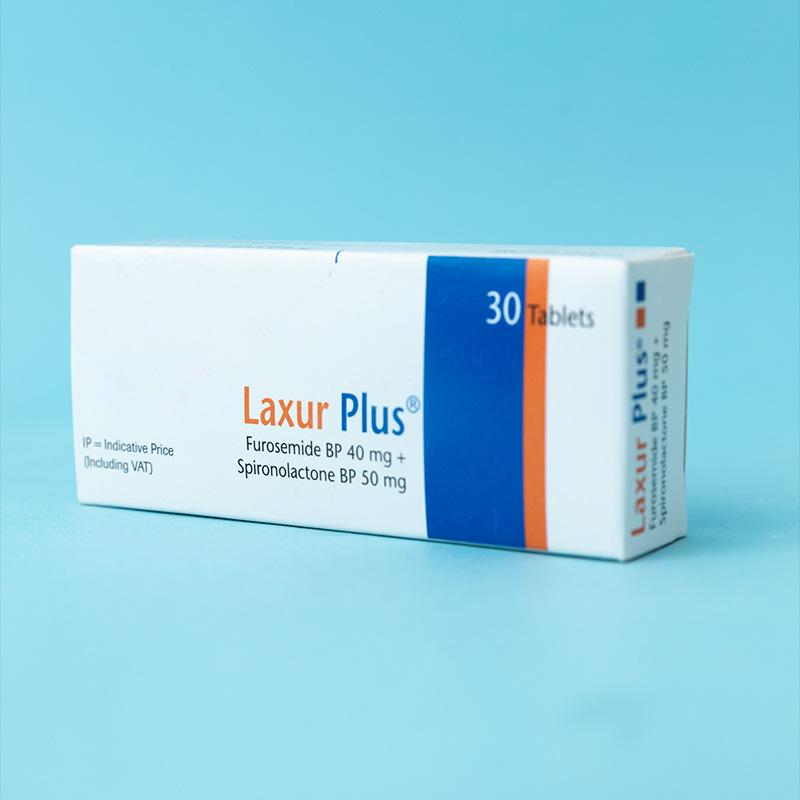
For the management of hypertension.

The recommended adult oral dosage is 5–10 mg once daily. The dosage can be increased up to 20 mg if needed or as directed by a physician.

Cilnidipine is contraindicated in patients with cardiogenic shock, recent myocardial infarction (MI) or acute unstable angina, and severe aortic stenosis.

Possible side effects include dizziness, flushing, headache, hypotension, peripheral edema, tachycardia, palpitations, gastrointestinal disturbances, increased micturition frequency, lethargy, eye pain, depression, ischemic chest pain, cerebral or myocardial ischemia, transient blindness, rashes, fever, abnormal liver function, gingival hyperplasia, myalgia, tremor, and impotence.

Caution is advised in patients with hypotension, poor cardiac reserve, or heart failure. Sudden withdrawal may exacerbate angina. Cilnidipine should be discontinued in patients who experience ischemic pain following administration.

Pregnancy: There is no specific information regarding the USFDA pregnancy category. Caution should be exercised when using Cilnidipine during pregnancy.
Lactation: Nursing mothers should consult a physician before taking Cilnidipine.

Cilnidipine may interact with other antihypertensives, aldesleukin, antipsychotics that cause hypotension, and medications that may modify insulin and glucose responses. It may also interact with quinidine, carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin, cimetidine, and erythromycin.

An overdose of Cilnidipine may cause excessive blood pressure reduction. If a significant drop in blood pressure occurs, appropriate measures such as lifting the lower extremities, fluid therapy, and administration of vasopressors should be taken.

Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C in a dry place. Protect from light and moisture.