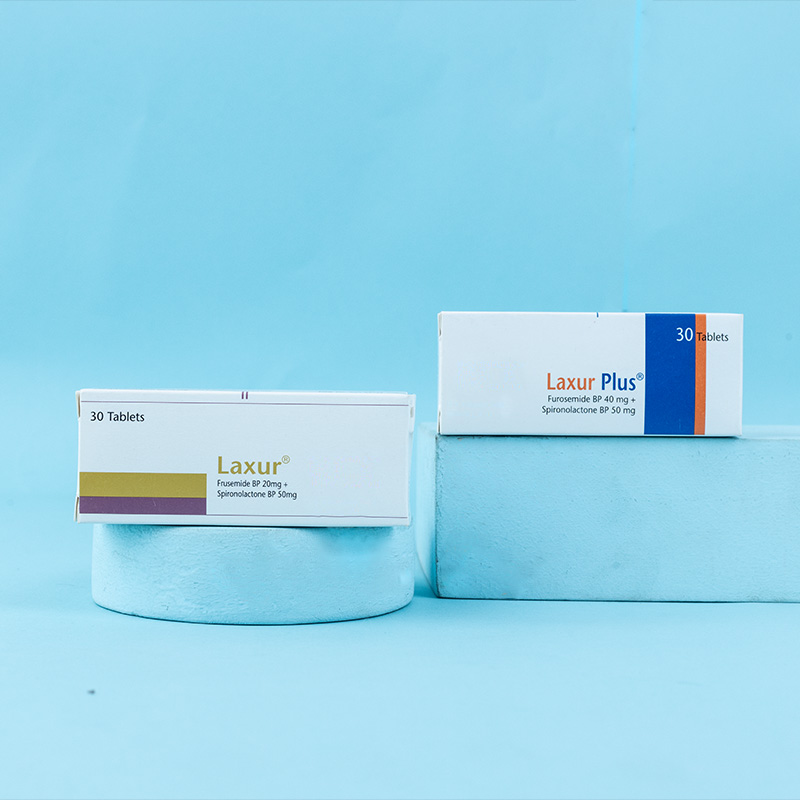
Laxur® is a combination diuretic containing a loop diuretic, frusemide, and a potassium-sparing diuretic, spironolactone. Spironolactone and frusemide have different but complementary mechanisms and sites of action. Therefore, when given together, they produce synergistic or additive diuretic effects. The frusemide component inhibits the Na+/K+/2Cl⁻ cotransporter in the ascending loop of Henle and blocks the reabsorption of sodium, potassium, and chloride ions, thereby increasing the quantity of sodium and the volume of water excreted in the urine. This characteristically induces potassium loss. The spironolactone component inhibits the reabsorption of sodium in exchange for potassium at the distal tubule by antagonizing the action of aldosterone, so that sodium excretion is greatly favored and the excess loss of potassium, induced by the frusemide, is reduced.

Frusemide: Frusemide is a short-acting diuretic; diuresis usually commences within one hour and lasts for four to six hours.
Spironolactone: Spironolactone, a competitive inhibitor of aldosterone, increases sodium excretion while reducing potassium loss at the distal renal tubule. It has a slow and prolonged action, with the maximum response usually attained after two to three days of treatment.

Laxur® is indicated for the treatment of:
● Essential hypertension
● Congestive heart failure
● Liver cirrhosis with fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity (ascites)
● Swelling due to excess fluid retention (edema)
● Overproduction of aldosterone (hyperaldosteronism)

1 to 4 tablets daily (50 to 200 mg of spironolactone and 20 to 80 mg of frusemide), according to the patient's response.

Adverse reactions associated with Laxur® include fatigue, blood disorders, skin rashes, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, hyperglycemia, hypotension, abnormal enlargement of breasts in males (gynecomastia), irregular menstrual cycles, and disturbances in electrolyte levels in the blood.

Laxur® is contraindicated in acute renal insufficiency, anuria, hyperkalemia, and in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to frusemide or spironolactone.

It is recommended that individuals taking this medicine have their fluid and salt (electrolyte) balance monitored regularly.
Laxur® should be used with caution in patients with diabetes, enlarged prostate (prostatic hypertrophy), hypotension, and low blood volume (hypovolemia).

Laxur® should be used with caution during pregnancy and only if the expected benefit to the mother is greater than the potential risk to the fetus.
Laxur® passes into breast milk. It is recommended that mothers avoid using this medicine while breastfeeding.

● When taken together with ACE inhibitors or potassium salts, there is an increased risk of hyperkalemia.
● Spironolactone increases blood levels of cardiac glycosides such as digoxin.
● Spironolactone decreases the ulcer-healing effects of carbenoxolone.
● Corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone may cause potassium loss, and severe depletion may occur if they are used with frusemide.
● When taken with drugs that lower blood pressure, there is an increased risk of a significant drop in blood pressure and fainting, especially with the first dose of ACE inhibitors (e.g., captopril).
● The blood pressure-lowering and diuretic effects of frusemide may be reduced or abolished when used with indomethacin or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).

Store in a cool, dry place below 30°C. Protect from light.
Medicine: Keep out of reach of children.