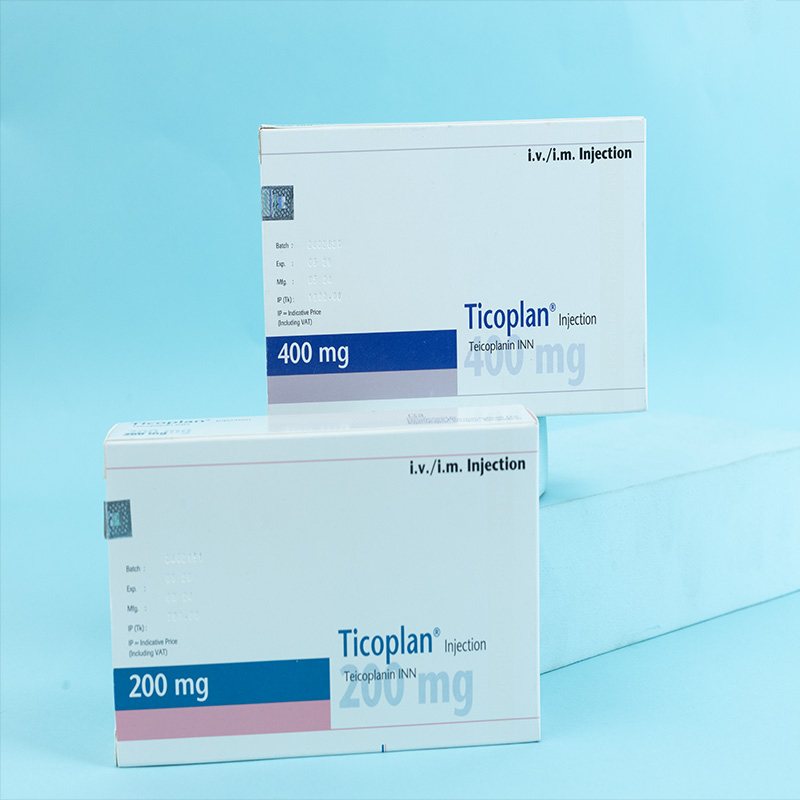
Teicoplanin is a glycopeptide antibiotic produced by Actinoplanes teichomyceticus. It is presented as a sterile, pyrogen-free, ivory-white powder for reconstitution with water for injection. Teicoplanin is freely soluble in water, and upon reconstitution, it forms a clear solution.

Teicoplanin inhibits the growth of susceptible organisms by interfering with cell wall biosynthesis at a site different from that affected by beta-lactams. It specifically binds to D-alanyl-D-alanine residues, blocking peptidoglycan synthesis.

Teicoplanin is indicated in adults and children for the treatment of the following infections:
Complicated skin and soft tissue infections.
Bone and joint infections.
Hospital-acquired pneumonia.
Community-acquired pneumonia.
Complicated urinary tract infections.
Infective endocarditis.
Teicoplanin is also indicated as an alternative oral treatment for Clostridium difficile infection-associated diarrhea and colitis. Where appropriate, Teicoplanin should be administered in combination with other antibacterial agents.

Teicoplanin can be administered intravenously (as a bolus injection or infusion) or intramuscularly. The intravenous injection may be given as a bolus over 3–5 minutes or as a 30-minute infusion. For neonates, only the infusion method should be used. The dosage depends on the severity of the infection and the patient's response to treatment.
Adults (Normal Kidney Function):
Standard dose: On the first day, 6 mg/kg (usually 400 mg) intravenously is recommended. Subsequent daily doses may be 6 mg/kg (400 mg) intravenously or 3 mg/kg (200 mg) intravenously or intramuscularly. Serious infections require the highest dose and intravenous administration.
Severe infections: Start with 6 mg/kg (400 mg) twice daily for 1–4 days (loading dose), followed by 6 mg/kg/day intravenously (maintenance dose).
Adults and Elderly (Kidney Failure):
Moderate kidney failure (creatinine clearance 40–60 ml/min): Halve the daily dose or administer on alternate days.
Severe kidney failure (creatinine clearance <40 ml/min) or hemodialysis patients: Reduce the daily dose to one-third or administer every three days.
For creatinine clearance ≤20 ml/min, treatment may proceed only with monitoring of blood drug levels.
Children (Normal Kidney Function):
Ages 2 months to 12 years: Start with 10 mg/kg every 12 hours for three doses, followed by 6–10 mg/kg/day. The highest dose is used for severe infections or neutropenic children.
Neonates (up to 2 months): Start with 16 mg/kg on the first day, followed by 8 mg/kg/day by slow intravenous infusion over approximately 30 minutes.
Children (Kidney Failure):
Follow the same dosage adjustments as for adults. Monitoring blood levels may help optimize treatment.
Clostridium difficile Infection-Associated Diarrhea
The recommended dose is 100–200 mg twice daily for 7–14 days.

Teicoplanin should be combined with another bactericidal antibiotic for infections requiring maximum bactericidal activity or when Gram-negative bacteria cannot be ruled out (e.g., empirical treatment of febrile neutropenia).
In most patients, Teicoplanin shows an effect within 48–72 hours. The total treatment duration depends on the infection type, severity, and patient response. For endocarditis and osteomyelitis, treatment for at least three weeks is recommended.

Inject 3 mL of water from the ampoule into the 200 mg or 400 mg Teicoplanin powder vial.
Gently rotate the vial between your hands until all the powder dissolves to prevent foaming.
If foam develops, allow the solution to stand for about 15 minutes until the foam disappears.
Use only clear, yellowish solutions for administration.

Sodium chloride 0.9%.
Ringer solution.
Ringer-lactate solution.
5% dextrose solution.
10% dextrose solution.
0.18% sodium chloride and 4% glucose solution.
0.45% sodium chloride and 5% glucose solution.

Teicoplanin is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug.

Use cautiously in patients hypersensitive to vancomycin due to possible cross-hypersensitivity.

Pregnancy: Category B3. Use during pregnancy or lactation only if potential benefits outweigh risks.

Local reactions: Erythema, injection site abscess (intramuscular).
Allergic reactions: Rash, pruritus, fever, shivering, anaphylactic reactions.
Gastrointestinal reactions: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
CNS reactions: Weakness, dizziness, headache.
Hearing reactions: Tinnitus, balance disorders.

Administer cautiously with nephrotoxic or ototoxic drugs, such as:
Aminoglycosides
Amphotericin B
Cyclosporine
Furosemide
Storage Conditions
Store below 30°C in a dry place, protected from light. Use reconstituted solutions immediately or refrigerate (2–8°C) for a maximum of 24 hours.