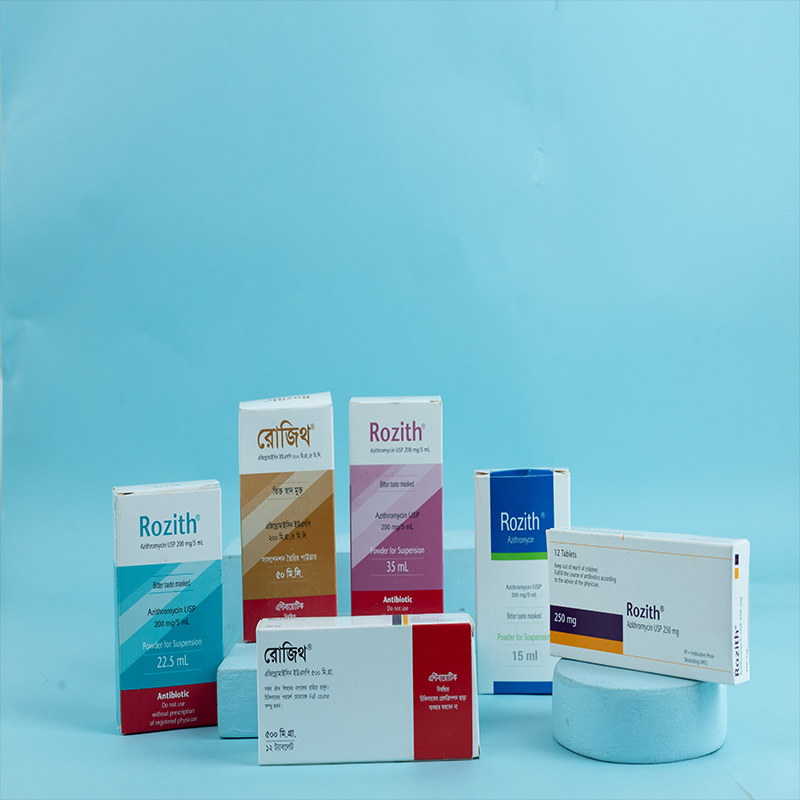
Rozith® 250 Tablet: Each film-coated tablet contains Azithromycin Dihydrate USP, equivalent to Azithromycin 250 mg.
Rozith® 500 Tablet: Each film-coated tablet contains Azithromycin Dihydrate USP, equivalent to Azithromycin 500 mg.
Rozith® Powder for Suspension: When reconstituted, each 5 ml suspension contains Azithromycin Dihydrate USP, equivalent to Azithromycin 200 mg.

Rozith® contains Azithromycin USP, an azalide antibiotic. Azithromycin works by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit of susceptible organisms, thereby interfering with microbial protein synthesis.

Rozith® is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to Azithromycin, Erythromycin, or any macrolide or ketolide antibiotics.

The liver is the principal route of elimination for Azithromycin. Caution is advised when administering Azithromycin to patients with impaired hepatic function.
If any allergic reaction occurs, discontinue the drug immediately and institute appropriate therapy.

Azithromycin is generally well-tolerated, with a low incidence of side effects. The most commonly reported adverse effects involve the gastrointestinal system, including diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, flatulence, and melena.
Allergic Reactions: Rash, edema, and urticaria have been reported. Rare cases of serious hypersensitivity reactions have also occurred.
Others: Transient and mild reductions in neutrophil counts have occasionally been observed in clinical trials, though a causal relationship with Azithromycin has not been established.

Pregnancy: Classified as Pregnancy Category B. Animal studies have not demonstrated harm to the fetus. However, animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human responses. Use Azithromycin during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers: It is unknown whether Azithromycin is excreted in human milk. Since many drugs are excreted in breast milk, exercise caution when administering Azithromycin to a nursing woman.

Azithromycin is safe and effective for the treatment of children aged 6 months and older.

With Other Medicines:
Careful monitoring is advised if Azithromycin is used concurrently with digoxin or ergot derivatives, as it may increase digoxin concentration and pose a theoretical risk of ergotism.
No pharmacokinetic interactions have been observed between Azithromycin and warfarin, theophylline, carbamazepine, methylprednisolone, or cimetidine.
With Food and Others:
Azithromycin absorption is reduced in the presence of food and antacids. Therefore, it should be administered 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals and antacids.

Adverse events resulting from higher-than-recommended doses are typically similar to those observed at normal doses but may occur more frequently. These include tinnitus and ototoxicity. In case of overdosage, provide general symptomatic and supportive measures as needed.

Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C in a dry place.
Protect from light and moisture.