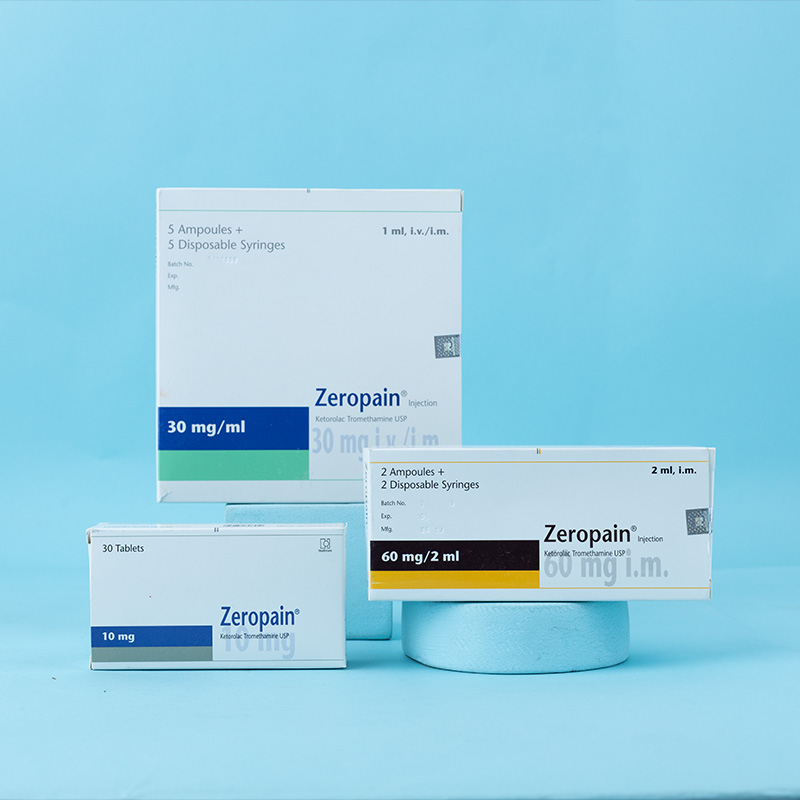
Zeropain® is a potent analgesic agent of the NSAID class. Its mode of action is to inhibit the cyclo-oxygenase enzyme system and hence prostaglandin synthesis, demonstrating a minimal anti-inflammatory effect at its analgesic dose. Plasma half-life is on average 5.3 hours in young adults and 7 hours in elderly patients (mean age 72). More than 99% of the ketorolac tromethamine in plasma is protein-bound over a wide concentration range.

Short-term management of moderate to severe acute pain that requires analgesia at the opioid level.

Usual dose: Adult: injection- 10-30 mg 4-6 hourly, maximum 5 days; tablet- 10 mg 4-6 hourly, maximum 7 days. Children (≥2 years): injection (I.V.)- 0.5 mg/kg 6 hourly, maximum 2 days; tablet- not established.

Note: When converting from parenteral to oral administration, total combined dose on the day of conversion should not exceed 120 mg (60 mg for 65 years of age or renally impaired or body mass <50 kg) of which the oral should not exceed 40 mg.

Opioid analgesics (e.g., morphine, pethidine) may be used concomitantly and may be required for optimal analgesic effect in the early postoperative period when pain is most severe. Ketorolac tromethamine does not interfere with opioid binding and does not exacerbate opioid-related respiratory depression or sedation.

Gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation related to previous NSAIDs therapy, severe heart failure, moderate to severe renal impairment, in labor and delivery, suspected or confirmed cerebrovascular bleeding, patients receiving ASA or other NSAIDs, and hypersensitivity to NSAIDs.

Use with other NSAIDs, coagulation disorder, hypertension, mild to moderate congestive heart failure, impaired renal function, asthma, liver dysfunction, skin rash, or any other sign of hypersensitivity. Patients receiving oral corticosteroids, warfarin, SSRIs, or antiplatelets.

Nausea, dyspepsia, gastrointestinal pain/bleeding, vomiting, hemorrhage, perforation, headache, sweating, dry mouth, acute renal failure, hyponatremia, bradycardia, hypertension, asthma, bronchospasm, rash, postoperative wound hemorrhage, abnormalities of liver function tests.

The safety of Ketorolac Tromethamine in human pregnancy has not been established. Pregnancy Category C, contraindicated in nursing mothers.

Children (≥2 years): injection (I.V.)- 0.5 mg/kg 6 hourly, maximum 2 days; tablet- not established.

Probenecid, lithium, other NSAIDs, ACE inhibitors.

Doses of 360 mg given intramuscularly over an 8-hour interval for five consecutive days have caused abdominal pain and peptic ulcers which have healed after discontinuation of dosing. Two patients recovered from unsuccessful suicide attempts. One patient experienced nausea after 210 mg ketorolac, and the other hyperventilation after 300 mg ketorolac.

Store at a temperature not exceeding 30ºC in a dry place. Protect from light.
Medicine: Keep out of reach of children.