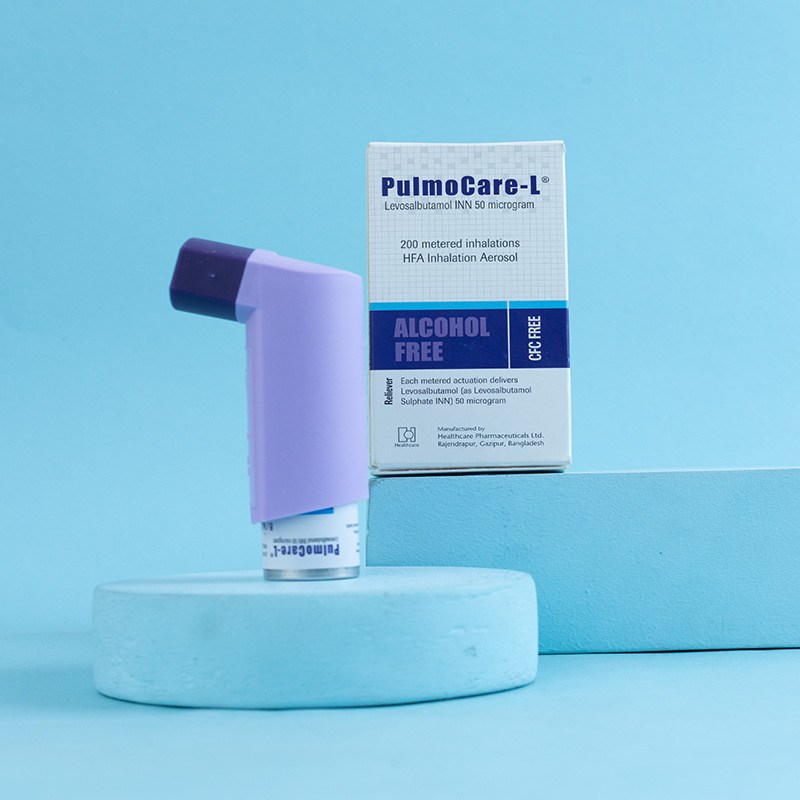
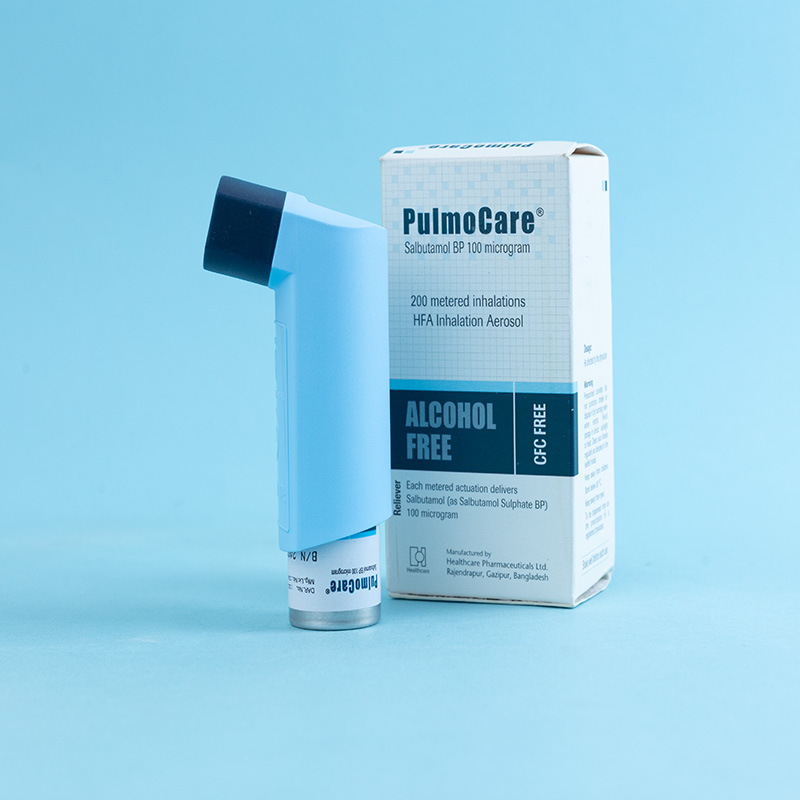
PulmoCare-L® inhaler is a pressurized metered-dose inhaler intended for oral inhalation only. It containsLevosalbutamol (as Levosalbutamol Sulphate INN) as the active ingredient, which is used in the treatment of bronchial asthma and reversible obstructive airway diseases. Levosalbutamol is a beta-adrenergic agonist that provides short-acting bronchodilation (4 to 6 hours) with a fast onset of action (5.5 to 10.2 minutes) in reversible airway diseases.

PulmoCare-L® inhaler is indicated for the treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in adults, adolescents, and children 4 years of age and older with reversible obstructive airway diseases.

For the treatment of acute bronchospasm episodes or prevention of asthmatic symptoms:
The usual dosage for adults and children (4 years and older) is 2 inhalations (100 mcg) every 4 to 6 hours.In some patients, 1 inhalation every 4 hours may be sufficient.More frequent administration or a higher number of inhalations is not routinely recommended. If a previously effective dosage regimen fails to provide the usual response, it may indicate worsening asthma and requires re-evaluation of the treatment regimen, with special consideration for anti-inflammatory treatment (e.g., corticosteroids).

PulmoCare-L® inhaler is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to levosalbutamol, racemic salbutamol, or any other component of PulmoCare-L®.Reactions may include urticaria, angioedema, rash, bronchospasm, anaphylaxis, and oropharyngeal edema.

Warnings and Precautions
Paradoxical Bronchospasm
PulmoCare-L® can cause paradoxical bronchospasm, which may be life-threatening. If this occurs, PulmoCare-L® should be discontinued immediately and an alternative therapy should be initiated. Paradoxical bronchospasm often occurs with the first use of a new canister.
Deterioration of Asthma
Asthma may worsen acutely within hours or chronically over several days. An increased need for PulmoCare-L® doses may indicate worsening asthma and requires reassessment of the patient’s condition and treatment plan. Consideration should be given to adding anti-inflammatory treatment (e.g., corticosteroids).
Like other beta-adrenergic agonists, PulmoCare-L® can cause significant cardiovascular effects, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure. Although uncommon at recommended doses, if cardiovascular effects occur, discontinuation of the drug may be necessary.
Beta agonists have also been reported to cause electrocardiogram (ECG) changes, such as flattening of the T wave, QTC interval prolongation, and ST segment depression. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Therefore, PulmoCare-L® should be used with caution in patients with coronary insufficiency, cardiac arrhythmias, or hypertension.
Hypokalemia: As with other beta-adrenergic agonists, PulmoCare-L® may cause significant hypokalemia, which could lead to adverse cardiovascular effects. This decrease is usually temporary and does not require supplementation.

PulmoCare-L® can cause serious side effects, including:
Sudden shortness of breath (bronchospasm)
Worsening asthma
Heart problems
Serious allergic reactions (swelling of the face, throat, or tongue; hives; rash; breathing problems)
Low potassium levels: The most common side effects include accidental injury, bronchitis, dizziness, pain, sore throat, runny nose, vomiting, palpitations, chest pain, fast heart rate, tremors, and nervousness.

Pregnancy Category C: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of PulmoCare-L® in pregnant women. Since animal studies are not always predictive of human response, PulmoCare-L® should only be used during pregnancy if the potential benefit outweighs the risk to the fetus.
Plasma concentrations of Levosalbutamol after inhalation of therapeutic doses are very low in humans. It is unknown whether Levosalbutamol is excreted in breast milk. Due to potential tumorigenicity observed in animal studies and the lack of sufficient data in nursing mothers, a decision should be made to either discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, considering its importance to the mother.

Avoid Concomitant Use
Other short-acting sympathomimetic aerosol bronchodilators or epinephrine should not be used alongside PulmoCare-L®.If additional adrenergic drugs are required, they should be used with caution to avoid potential cardiovascular effects.
Beta-Blockers: Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers may counteract PulmoCare-L®'s effect and induce severe bronchospasm in asthmatic patients.
Cardioselective beta-blockers should only be used when no alternatives are available and with extreme caution.
Diuretics: PulmoCare-L® may exacerbate ECG changes or hypokalemia caused by non-potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., loop or thiazide diuretics).Potassium levels should be monitored if used together.
Digoxin: Studies have shown a 16–22% decrease in serum digoxin levels after administration of racemic salbutamol.
Monitoring serum digoxin levels is advised when used concomitantly.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) or Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
PulmoCare-L® should be used with extreme caution in patients currently taking MAOIs or TCAs or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such drugs.
Consider alternative therapy to avoid potential vascular effects.

Symptoms of PulmoCare-L® overdosage include:
Seizures, angina, hypertension/hypotension, tachycardia (up to 200 bpm), arrhythmias, nervousness, tremors, dizziness, fatigue, nausea, dry mouth, palpitations, malaise, and sleeplessness.Severe overdosage can lead to cardiac arrest and death.
Treatment:
Discontinue PulmoCare-L® immediately.
Consider cardioselective beta-receptor blockers (with caution, as they may cause bronchospasm).
Dialysis effectiveness in overdosage is unknown.

Pressurized canister: Do not puncture, break, or incinerate, even when empty.
Avoid direct sunlight or heat.
Store below 30°C.
Keep away from eyes and children