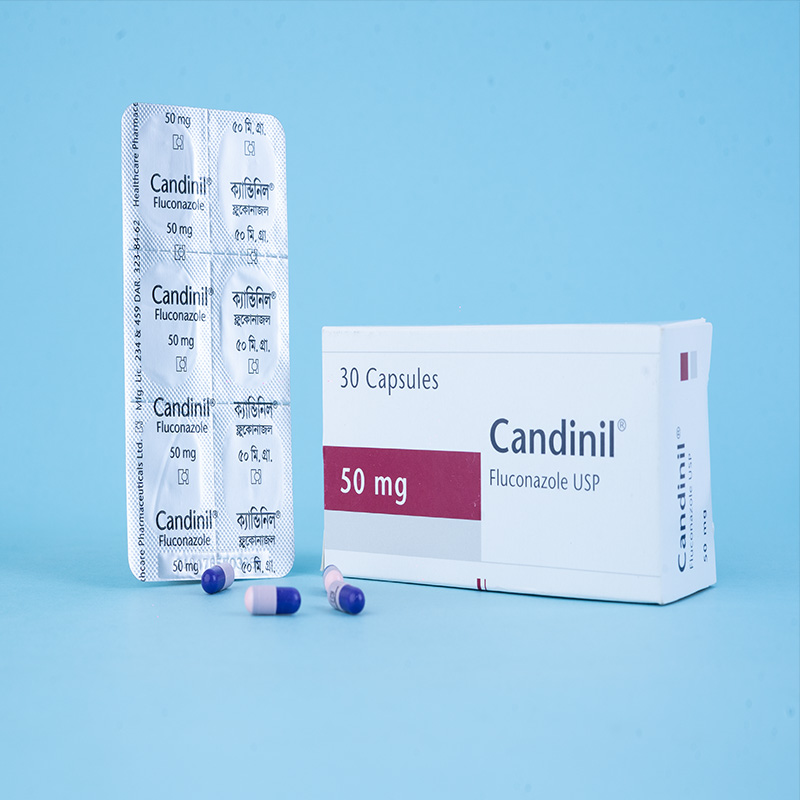
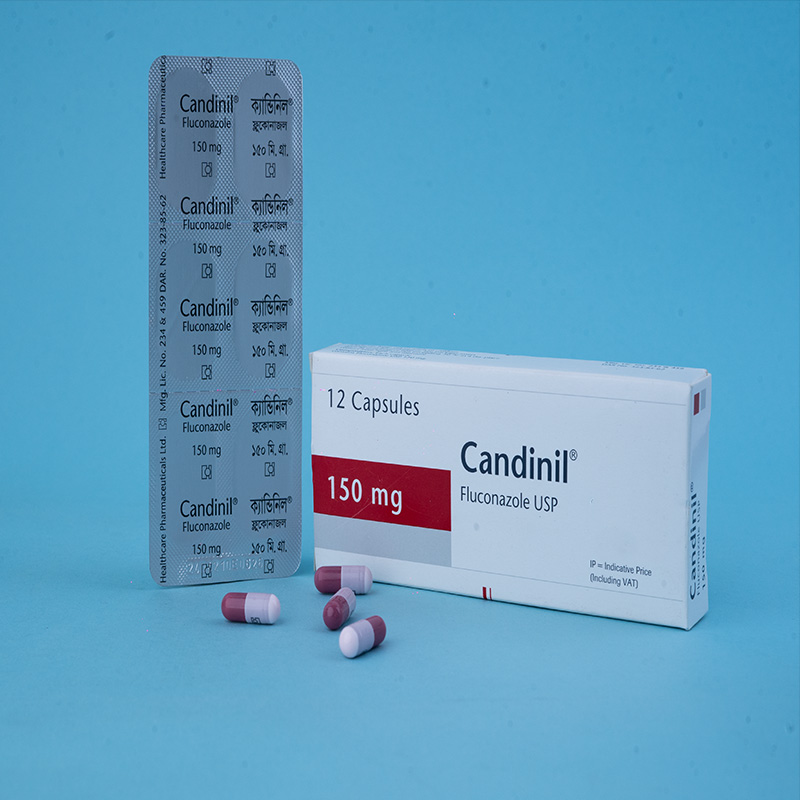
Candinil® Suspension: After reconstitution, each 5 ml suspension contains Fluconazole USP 50 mg.

Fluconazole is a synthetic triazole antifungal drug that inhibits the biosynthesis of ergosterol, a major component of the cell membrane in yeast and fungal cells. This leads to abnormalities in membrane permeability, inhibition of growth, abnormal cell wall formation, and accumulation of intracellular lipids and membranous vesicles. It is effective against a broad spectrum of yeast and other fungal pathogens.
Following oral administration, absorption is rapid, with more than 90% of the dose being absorbed. Bioavailability remains the same whether taken on an empty stomach or with food, as the pharmacokinetics of Fluconazole are relatively unaffected by physiological changes in the gastrointestinal tract. Unlike other azole drugs, the bioavailability of Fluconazole is not influenced by gastric pH, allowing it to be used alongside antiulcer drugs, including PPIs.
Approximately 80% of a Fluconazole dose is excreted unchanged, and 11% is excreted as inactive metabolites in the urine, presumably due to liver metabolism. An additional 2% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the feces, while the fate of the remainder is unknown.

- Superficial candidal infections, such as oral or vaginal thrush
- Esophagitis caused by Candida or other susceptible species
- Maintenance therapy for cryptococcal meningitis
- Disseminated candidiasis
- Prophylaxis of fungal infections in neutropenic cancer patients
- Acute treatment of other systemic fungal infections
- Dermatophyte and Candida skin infections

Fluconazole is usually administered orally. The total daily dose is generally given at once unless nausea occurs, in which case the dose may be divided.
Vaginal candidiasis and candidal balanitis: 150 mg as a single oral dose.
Mucosal candidiasis (excluding genital): 50 mg orally daily (100 mg daily for severe infections) for 7–14 days for oropharyngeal candidiasis; 14–30 days for other mucosal infections (e.g., esophagitis, candiduria, or non-invasive bronchopulmonary infections).
Children: 6 mg/kg orally on the first day, then 3 mg/kg daily for a total of 14–21 days (every 72 hours in neonates up to 2 weeks old and every 48 hours in neonates aged 2–4 weeks).
Tinea pedis, corporis, cruris, pityriasis versicolor, and dermal candidiasis: 50 mg orally daily for 2–4 weeks (up to 6 weeks for tinea pedis; maximum treatment duration is 6 weeks).
Invasive candidal infections, including candidemia and disseminated candidiasis, and cryptococcal infections, including meningitis: 400 mg orally initially, followed by 200 mg daily. The dose may be increased to 400 mg daily if necessary. Treatment should continue based on the response, lasting at least 6–8 weeks for cryptococcal meningitis.
Children: 6–12 mg/kg daily (every 72 hours in neonates up to 2 weeks old, every 48 hours in neonates aged 2–4 weeks); maximum 400 mg daily.
Prevention of cryptococcal meningitis relapse: 100–200 mg orally daily.
Prevention of fungal infections in immunocompromised patients following chemotherapy or radiotherapy: 50–400 mg orally daily, adjusted based on risk.
Children: 3–12 mg/kg daily (every 72 hours in neonates up to 2 weeks old, every 48 hours in neonates aged 2–4 weeks); maximum 400 mg daily.

Common side effects include nausea, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, flatulence, headache, and rash. Less common effects include dyspepsia, vomiting, abnormalities in liver enzymes, seizures, alopecia, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.

Renal impairment: Use with caution.
Hepatic disease: Monitor liver function and discontinue use if signs or symptoms of liver dysfunction appear.

Limited data are available on the use of Fluconazole during pregnancy. It should be used in pregnancy only when the benefits clearly outweigh the risks.
Fluconazole is excreted in breast milk at levels approximately half of those in plasma. It should, therefore, be avoided during lactation.

Fluconazole decreases the metabolism of Cyclosporine and Phenytoin and increases the AUC of Retinoic acid.
Fluconazole increases bleeding time in patients treated with Warfarin.
Concomitant use reduces the clearance of Theophylline and increases plasma levels of Zidovudine and oral hypoglycemics.
Rifampin induces Fluconazole metabolism.

In case of an overdose, supportive measures should be taken.

Candinil® Suspension: Bottles of dry powder for reconstitution to 35 ml suspension.

Store in a cool, dry place below 30ºC. Protect from light and moisture.
Medicine: Keep out of reach of children.