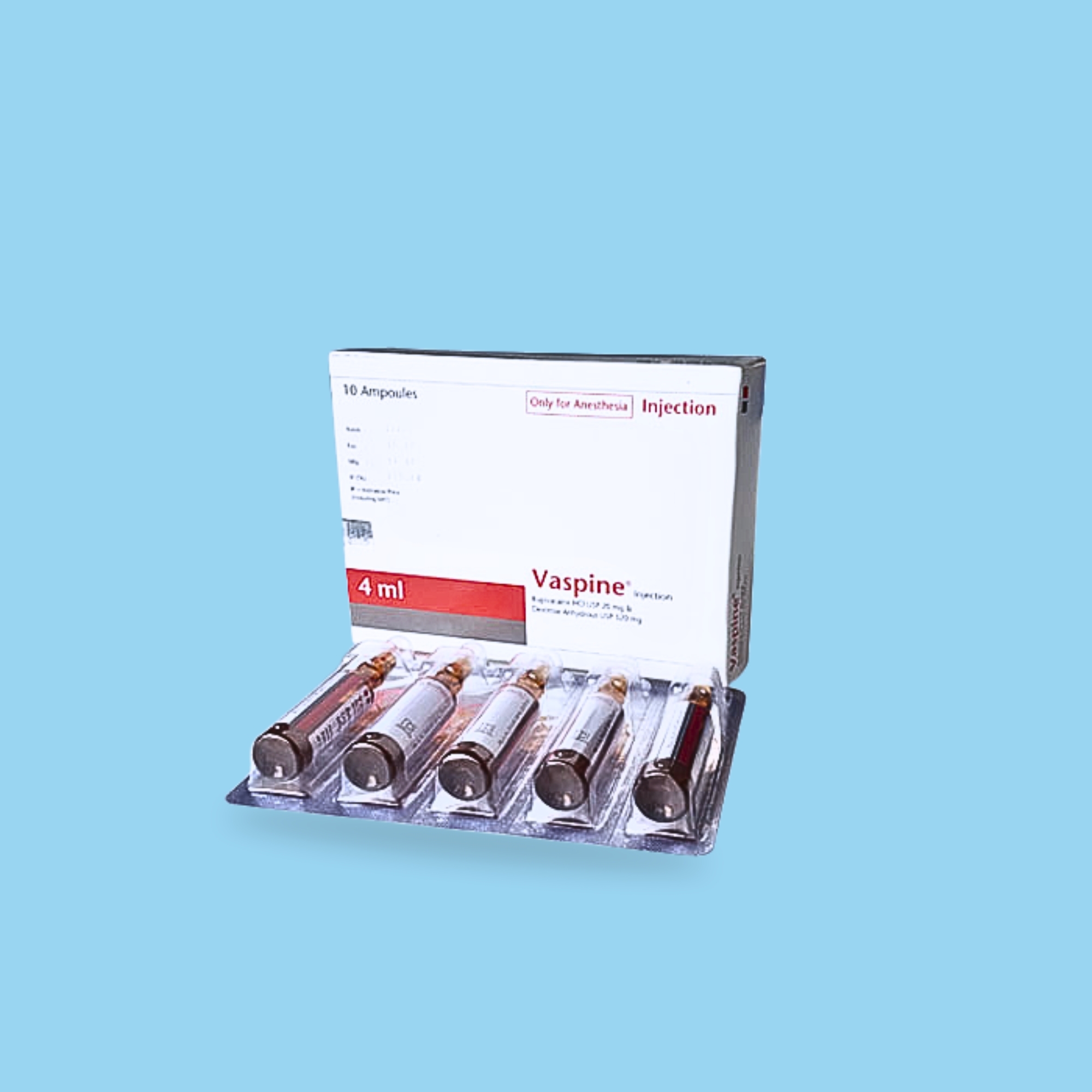
Bupivacaine is indicated for lower abdominal surgery (including Caesarean section), urological and lower limb surgery, including hip surgery, lasting 1.5 to 3 hours. Bupivacaine is indicated for intrathecal (subarachnoid, spinal) anesthesia for surgical and obstetrical procedures. Bupivacaine produces motor blockade of the abdominal muscles, making the solution suitable for abdominal surgery lasting 1.5-2 hours. The duration of motor blockade does not exceed the duration of analgesia.

The following dosage recommendations should be regarded as a guide for use in the average adult:
Spinal anesthesia for surgery: 2-4 ml (10-20 mg Bupivacaine hydrochloride). The patient's physical status and concomitant medication should be considered when deciding the dose, and the lowest dose required for adequate anesthesia should be used. Duration varies with dose, while segmental spread may be difficult to predict, especially with the isobaric (plain) solution. The dose should be reduced in the elderly and in patients in the late stages of pregnancy.
Pediatrics
Bupivacaine may be used in children. One of the differences between small children and adults is a relatively high CSF volume in infants and neonates, requiring a relatively larger dose per kg to produce the same level of block as compared to adults.
< 5 kg: 0.40-0.50 mg/kg
5 to 15 kg: 0.30-0.40 mg/kg
15 to 40 kg: 0.25-0.30 mg/kg

The adverse reaction profile for Bupivacaine is similar to those for other long-acting local anesthetics administered intrathecally. Adverse reactions caused by the drug itself are difficult to distinguish from the physiological effects of the nerve block (e.g., decrease in blood pressure, bradycardia, temporary urinary retention), events caused directly (e.g., nerve trauma) or indirectly (e.g., epidural abscess) by the needle puncture, or events associated with cerebrospinal leakage.

General contraindications related to intrathecal anesthesia should be taken into account.
Absolute
Allergy or hypersensitivity to amide-type local anesthetics. Detection of suspected sensitivity by skin testing is of limited value.
Acute active diseases of the cerebrospinal system, such as meningitis, tumors (primary or secondary), poliomyelitis, subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord, cranial hemorrhage, demyelinating disease, and raised intracranial pressure.
Spinal stenosis and active disease or recent trauma in the vertebral column.
Relative
Arthritis and other diseases of the vertebral column are relative contraindications due to technical difficulties in performing a spinal injection.

It is reasonable to assume that a large number of pregnant women and women of childbearing age have been given Bupivacaine. No specific disturbances to the reproductive process have been reported, such as an increased incidence of malformations. However, the dose should be reduced in patients in the late stages of pregnancy. With recommended doses, Bupivacaine enters breast milk in such small quantities that there is generally no risk of affecting the breastfed child.
At maternal serum levels of up to 0.45 g/mL, produced by the epidural use of Bupivacaine for vaginal delivery, Bupivacaine could not be detected in breast milk during the first 24 hours after delivery (detection limit 0.02 g/mL).

Acute emergencies associated with the use of local anesthetics are generally related to high plasma levels. Since the dose required for spinal anesthesia is so small (20% or less than that required for epidural anesthesia), acute systemic toxicity is extremely unlikely and has not been reported.
With accidental intravascular injections of local anesthetics, toxic effects will be obvious within 1-3 minutes. With overdose, peak plasma concentrations may not be reached for 20-30 minutes, depending on the site of injection, and toxic signs will be delayed. Toxic reactions mainly involve the central nervous and cardiovascular systems.

Local anesthetics react with certain metals and cause the release of their respective ions, which, if injected, may cause severe local irritation. The ampoules are designed for single use only; any unused portions of the solution should be discarded. The solution should be used immediately after opening the ampoule. Solutions showing discoloration should not be used.

Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C in a dry place. Protect from light. Medicine: Keep out of reach of children.