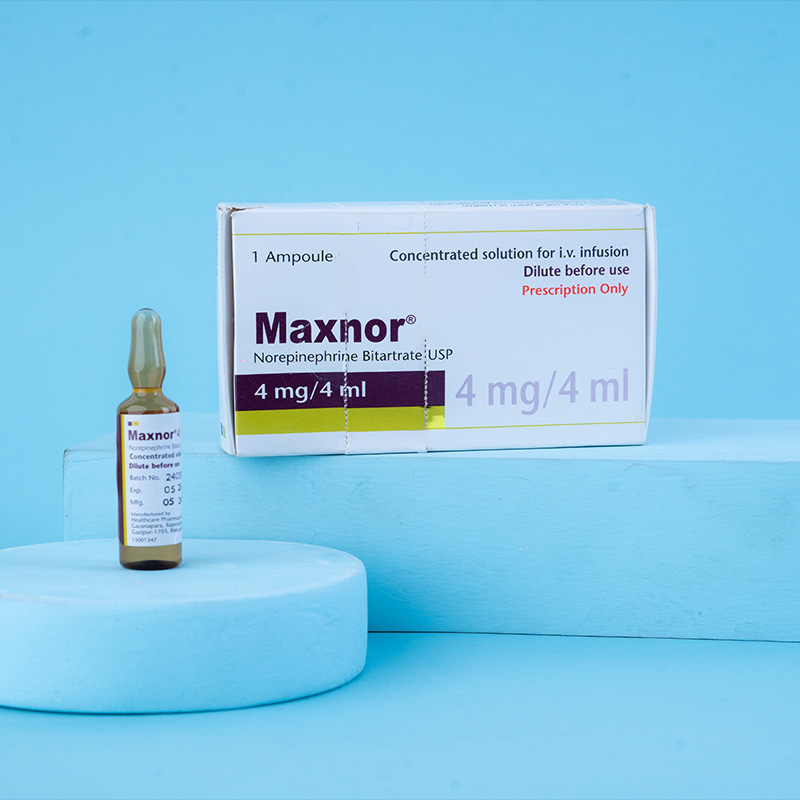
Maxnor® functions as a peripheral vasoconstrictor (alpha-adrenergic action) and an inotropic stimulator of the heart and dilator of coronary arteries (beta-adrenergic action).

Maxnor® is used for blood pressure control in certain acute hypotensive states, such as pheochromocytomectomy, sympathectomy, poliomyelitis, spinal anesthesia, myocardial infarction, septicemia, blood transfusion, and drug reactions. It is also used as an adjunctive treatment in cardiac arrest and profound hypotension.

Maxnor® should be administered via intravenous infusion into a large vein.
Restoration of Blood Pressure in Acute Hypotensive States. Blood volume depletion should always be corrected as fully as possible before administering any vasopressor. However, when immediate intra-aortic pressure maintenance is required to prevent cerebral or coronary artery ischemia, Maxnor® may be administered before and concurrently with blood volume replacement.
Dilution: Maxnor® should be diluted in 5% dextrose injection or 5% dextrose with sodium chloride injection to prevent oxidation-related potency loss. Saline solution alone is not recommended. If blood or plasma is required to increase blood volume, it should be administered separately using a Y-tube and individual containers.
Average Dosage: Add one ampoule (4 mg/4 mL) of Maxnor® to 1,000 mL of a 5% dextrose-containing solution. Each mL of the diluted solution contains 4 mcg of Maxnor® base. The infusion should be administered intravenously, using a plastic IV catheter inserted through a suitable bore needle well-advanced into the vein and securely fixed with adhesive tape.
An IV drip chamber or another metering device should be used to ensure accurate control of the infusion rate. The initial dose is 2 to 3 mL per minute (8 to 12 mcg of Maxnor® base). The infusion rate should then be adjusted to maintain a low normal systolic blood pressure (80–100 mmHg), ensuring adequate circulation to vital organs.
For hypertensive patients, blood pressure should be raised no higher than 40 mmHg below their preexisting systolic pressure.
Maintenance Dosage: The average maintenance dose ranges between 0.5 to 1 mL per minute (2 to 4 mcg of Maxnor® base).
High Dosage: In some cases, larger doses (up to 68 mg per day or 17 ampoules) may be required if hypotension persists. However, occult blood volume depletion should always be suspected and corrected if present. Central venous pressure monitoring is useful in detecting and managing this condition.
Fluid Intake: Dilution should be adjusted based on fluid volume requirements. If large volumes of dextrose are required, a more diluted solution may be necessary to avoid excessive drug dosage. Conversely, if fluid restriction is needed, a higher concentration of Maxnor® may be used.
Duration of Therapy: The infusion should continue until blood pressure and tissue perfusion are maintained without therapy. Maxnor® should be tapered off gradually to avoid abrupt withdrawal effects. In cases of vascular collapse due to acute myocardial infarction, therapy may be required for up to six days.
Adjunctive Treatment in Cardiac Arrest: Maxnor® is administered intravenously during cardiac resuscitation to maintain adequate blood pressure after restoring a heartbeat and ventilation. Its beta-adrenergic action enhances systolic contraction strength.
Dosage: The same dosing guidelines as those for acute hypotensive states should be followed.
Important Precaution: Do not use Maxnor® if the solution is pinkish or darker than slightly yellow or if it contains precipitates. Avoid contact with iron salts, alkalis, or oxidizing agents.

Maxnor® should not be used in patients with hypotension due to blood volume deficits, except as an emergency measure to maintain coronary and cerebral artery perfusion until blood volume replacement is completed.
Prolonged administration without blood volume replacement can cause:
Severe vasoconstriction (peripheral & visceral)
Reduced renal perfusion & urine output
Tissue hypoxia & lactic acidosis
Maxnor® is contraindicated in patients with mesenteric or peripheral vascular thrombosis, as it may worsen ischemia and expand the infarcted area.

Maxnor® should not be used with cyclopropane or halothane anesthesia, as these agents increase myocardial sensitivity, leading to a risk of ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation. The same risk applies to patients with profound hypoxia or hypercarbia.

Hypertension Risk
Maxnor® is a potent vasopressor, and responses vary among patients. Overdose may cause severe hypertension, so blood pressure should be:
Monitored every two minutes initially
Monitored every five minutes if infusion is continued
Patients must not be left unattended while receiving Maxnor®. Headache may indicate overdosage-related hypertension.
Extravasation Precautions: Frequent monitoring of the infusion site is required to avoid extravasation, which may lead to local necrosis due to vasoconstriction.
If extravasation occurs, antidote treatment with 10–15 mL of saline solution containing 5–10 mg of phentolamine should be injected into the affected area as soon as possible.

Common Reactions
Ischemic injury (due to vasoconstriction & hypoxia)
Bradycardia (reflex response to increased BP)
Arrhythmias, anxiety, transient headache
Respiratory difficulty
Extravasation necrosis at the injection site
Long-term use may cause plasma volume depletion, leading to severe vasoconstriction, reduced renal perfusion, and ischemic injury. Gangrene of extremities has been rarely reported.

Pregnancy (Category C): Maxnor® should only be used if clearly necessary, as no animal reproduction studies have been conducted.
Lactation: It is unknown whether Maxnor® is excreted in breast milk. Use with caution in nursing mothers.
Pediatrics: Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatrics: Elderly patients may have decreased renal, hepatic, or cardiac function. A lower starting dose is recommended. Infusion into leg veins should be avoided in elderly patients.

Maxnor® interacts with:
Cyclopropane & halothane anesthesia → Risk of ventricular arrhythmias
MAO inhibitors & tricyclic antidepressants → Risk of severe hypertension

Overdose symptoms include severe hypertension, reflex bradycardia, increased peripheral resistance, and reduced cardiac output. Treatment involves stopping Maxnor® infusion and stabilizing blood pressure.

Storage: Keep below 30°C in a dry place, protected from light.
Caution: Keep out of reach of children.